The promise of AI builders like Bolt.Ai is compelling: convert a text prompt into a functional web application in minutes. It is an amazing tool for rapid prototyping, which is why the company behind it has experienced explosive growth, soaring to over $40 million in Annual Recurring Revenue (ARR) in a matter of months.
However, if you’re like many developers or technical founders, your Bolt project is now stuck: a messy prototype with broken components, an unresponsive AI, or a codebase maxed out on context. This isn’t a failure of the technology; it’s a failure in prompt engineering and project management.
Here are the core reasons your project stalled and the practical, code-first strategies to get it to the finish line immediately.
The Top 3 Reasons Your AI Prototype Is Stuck
The challenges in AI-assisted coding typically stem from mismanaging the AI’s core limitations: its memory, its input size, and its inability to perform complex project management.
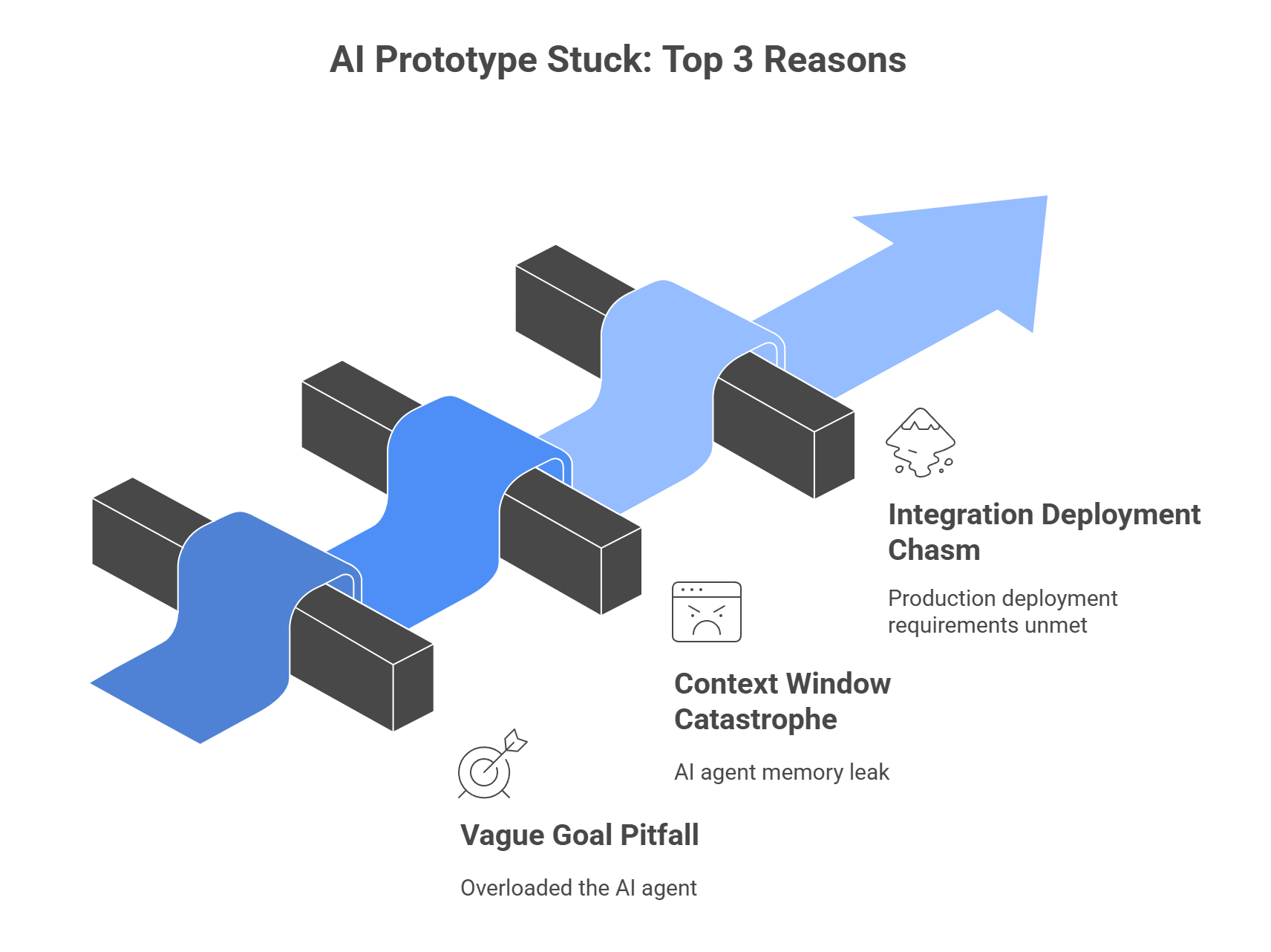
1. The Vague Goal Pitfall: You Overloaded the Agent
The single greatest cause of failure is asking the AI to build too much at once.
The Problem: You wrote one prompt: “Build a full-stack job board app with user authentication, a search filter, a job posting form, and connect it to Supabase.“ The AI successfully creates the first few components (the homepage and form), but it quickly loses context of the entire codebase. Subsequent changes break existing features or lead to incomplete logic.
The Developer Fix: The Atomic Prompt Rule
Treat the AI as a highly focused junior developer. Break your overall plan into the smallest possible, sequential tasks.
Rule: One feature, one prompt. Confirm it works before moving on.
Example Sequence:
- “Create a React component for the main job listing card with Tailwind CSS.”
- “Now, create the parent JobList component to render 10 of these cards using dummy data.”
- “Replace the dummy data with actual data fetched from the Supabase jobs table, handling loading and error states.”
2. The Context Window Catastrophe (AI Memory Leak)
The AI agent has a limited “memory” (context window) that includes your project’s code, files, dependencies, and all previous chat history.
The Problem: Once your project exceeds a certain size, the AI literally cannot read all the code required for a change. This results in the dreaded “AI stuck,” “project exceeds context,” or, worst of all, the AI deleting or overwriting code it “forgot” was there.
The Developer Fix: Code Isolation and Hygiene
To reclaim context space and stabilize the project:
- The Nuclear Option (The Reset): Duplicate your project. This instantly clears the bloated chat history, often giving the AI the fresh memory needed to complete the final steps.
- Use
.bolt/ignore: For static files, assets, or completed module folders (e.g.,/lib/config, /assets/images), use the .bolt/ignorefile to exclude them from the AI’s attention, dramatically reducing the context load. - Manual Cleanup: Run dependency cleaners to remove unused packages. If you are developing a custom web application development services that requires complex logic, manually review your modules and ensure all utility functions are in discrete, clean files.
3. The Integration and Deployment Chasm
The difference between a working prototype in the browser and a live, scalable application is significant.
The Problem: The AI excels at front-end code but often struggles with the robust requirements of production deployment: complex database queries, scalable backend logic, and environment variable security. You might find yourself needing to hire MySQL developers to optimize slow database calls that the AI generated.
The Developer Fix: Production-First Mindset
- Environment Variables: Never hardcode API keys. Explicitly instruct the AI: “When connecting to Stripe, use
process.env.STRIPE_SECRET_KEYand do not store the key in any file.” - Validate the Build: Before your final deploy, open the terminal and manually run the build script (
npm run buildor similar) to catch local build errors before they break your Netlify/Vercel deployment.
Your 5-Step Rapid Launch Plan
If you’re stalled at 80% completion, follow this checklist to push your app live within hours.
|
Step |
Action |
Why It Works |
| 1. Stabilize the Environment | Duplicate the project immediately to clear the AI’s memory and resolve the “Stuck AI” error. Work only in the copy. | Provides the AI with a clean, low-context environment for the final crucial steps. |
| 2. Target the Broken Feature | Ask the AI to explain the function of the broken component, then paste the explanation and code into a general LLM (like Gemini or ChatGPT) for a suggested fix. | Bypasses Bolt’s limitations for pure code debugging. You manually integrate the fixed code back into Bolt. |
| 3. Clean the Backend Connection | If the database is slow or broken, isolate the data fetching module. Ask Bolt to optimize the query for efficiency. | Addresses the root cause of production delays often overlooked by generalist AI agents. |
| 4. Check Mobile Responsiveness | Before deployment, ask Bolt to specifically review and fix the application’s layout for mobile devices using current best practices. If your goal is to hire mobile application developer quality code, you need to be explicit. | Ensures a polished, professional UX across all devices, preventing immediate user complaints post-launch. |
| 5. Final Deployment Prep | Ask Bolt: “Generate a final review of the deployment configuration, confirming all environment variables are correctly referenced and the build script is error-free.” | Mitigates the most common failure point for moving a prototype to production. |
Project Rescue: How YES IT Labs Can Guarantee Your Launch
Bolt.Ai is brilliant for generating the first 80% of a web application. The final 20%, the state management, edge cases, scalability, security, and complex business logic, is where expertise matters.
If your project is mission-critical, over budget on tokens, or beyond simple fixes, YES IT Labs offers specialized technical services to transition your prototype into a robust, scalable product.
|
YES IT Labs AI Project Acceleration Services |
Value Proposition |
| Code Review & Stabilization | Our senior developers inherit your AI-generated code, stabilize recurring bugs, implement robust error handling, and refactor the architecture for maintainability and lower operating costs. |
| Complex Backend Integration | We specialize in connecting your front-end to advanced, custom backend services, ensuring seamless integration with third-party APIs (payment, analytics, ERPs) and complex authentication systems. |
| Scalable Deployment Assurance | We set up professional Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) pipelines, handle secure cloud configuration, and ensure your application is ready to scale from day one. |
| Expert Consulting & Training | We provide expert guidance on refining your prompts and managing your AI-assisted workflow, turning your team into “AI Whisperers” to prevent future bottlenecks. |
Don’t let a great prototype die at the finish line. Partner with the experts who can fix the last 20% and guarantee your launch.
Top 5 FAQs for Stalled Bolt.Ai Projects
1. The AI deleted a feature I didn’t ask it to change. Why did this happen and how do I get the code back?
This is a classic Context Window overflow issue. The AI’s internal memory couldn’t hold your entire project, so when it made a change, it literally forgot the function or component you didn’t mention and replaced the file with an incomplete version.
The Fix:
- Do Not Prompt Again: Stop trying to fix the deletion with a new prompt; you risk losing more code.
- Use the Rollback: Immediately check Bolt’s version history or local file comparison feature (often available in the UI or via Git if you connected early) and rollback the affected file to the last working state before the deletion occurred.
- Isolate the File: Once the code is restored, use the “Target File” feature (if available) or simply paste the full, working code of the restored file back into the chat. Then, specifically ask the AI to make the change only to the one component, ensuring it has the full context of that file.
2. My project is using too many tokens, and costs are spiking. How do I reduce AI processing costs?
High token usage is a direct result of the Context Window Size and inefficient prompting. Every time the AI runs, it re-reads all the files in its scope.
The Fix:
- Aggressively Use
.bolt/ignore: This is your primary cost-saving tool. Exclude large, completed folders like utility libraries, image assets, or finished pages (e.g.,/pages/about,/styles). The less code the AI has to read per prompt, the fewer tokens you use. - The Duplicate Reset: Clearing the chat history by Duplicating the project is essential. The conversation history itself consumes a large number of tokens.
- Code for AI Efficiency: Ask the AI to refactor large components into smaller, reusable pieces. Smaller files mean the AI can be prompted to read only the required file, drastically reducing tokens per request.
3. The AI keeps making the same logical mistake (e.g., using the wrong prop name). How do I force it to learn?
This happens because the AI’s current context is fixated on an outdated piece of code or an incorrect function signature. It is stuck in a self-reinforcing loop.
The Fix:
- Manual Override and Re-teaching: Do not ask the AI to fix the bug. Instead, go into the file, manually correct the mistake, and then use a zero-change prompt: “I have corrected the UserCard component to use the userId prop instead of userIdentifier. Please acknowledge this change and confirm the component is correct.”
- Target the Source: If the error is repeated across files, find the root file (e.g., the TypeScript interface or the utility function) and ask the AI to fix the source definition first.
4. I need to integrate a custom API (not Supabase/Stripe). The AI fails every time. What is the developer solution?
The AI works best with popular, well-documented services. Custom or internal APIs require structured data the AI can ingest.
The Fix: Provide Schema and Examples
Give it the Schema: Don’t just give the endpoint. Provide the AI with the complete request and response schema in a clean, easily parsable format (e.g., a simple JSON object):
JSON
// Custom API Schema for /api/getOrders
// Request: { "userId": 123 }
// Response: [{ "orderId": 7, "status": "shipped" }]
- Isolate the Integration: Ask the AI to write a separate, small utility function (e.g.,
src/utils/customApi.js) solely for handling the fetch, parsing, and error handling for the custom API. Once this single file is correct, you can use it confidently throughout the rest of your app.
5. My app runs perfectly in Bolt, but when I deploy, the database connection fails. How do I debug the production environment?
This is almost always an Environment Variable and Build issue. The Bolt environment is running with local tokens/settings, but the deployed app is not receiving them correctly.
The Fix: Validate Environment & Build Output
- Check the Host: Ensure your database security rules (e.g., in Supabase) whitelist the URL of your deployed app (e.g.,
https://my-app.netlify.app). Bolt’s environment has a different origin. - Inspect the Deployed Logs: Go to your deployment host (Netlify, Vercel) dashboard and check the build logs. Look for warnings or errors related to missing variables like
VITE_SUPABASE_KEYorDATABASE_URL. - Verify Variable Access: In your code, you should be using
process.env.VARIABLE_NAME. If you are using React/Vite, ensure variables are prefixed correctly (e.g., VITE_). A quick prompt to the AI is: “Verify that all environment variables are being accessed correctly in the code for a production build.