There is something exciting about opening WeWeb for the first time. The clean interface, the visual builder, the idea that you can create a real web application without touching code feels incredibly empowering. Many business owners start their project feeling motivated and optimistic, convinced that this is the tool that finally gives them control.
But after the initial excitement wears off, reality usually hits. Pages do not behave the way you want. Features break unexpectedly. And suddenly a project that felt simple turns into hours of trial and error. You are not alone in that feeling. A recent no code adoption report found that more than half of WeWeb users eventually ask a professional for help, usually after getting stuck on something they did not anticipate.
If you are somewhere in the middle of that journey, feeling a bit overwhelmed or unsure what to fix next, this is exactly for you. Let’s talk about the hidden challenges people run into and the moments when calling a professional saves not just time but sanity.
1. When Logic Doesn’t Behave the Way You Expected
At first, building workflows in WeWeb feels straightforward. Add an action here, set a condition there, connect it to your data source. Easy. But as your app grows and you start stacking conditions, triggers, and dynamic states, the logic becomes harder to follow.
Suddenly:
- Buttons stop responding.
- A workflow runs out of order.
- A condition overrides something else.
- Data displays differently depending on the user.
Many people start their project after exploring custom web application development services, assuming no code will be simpler. The truth is that once your app grows, the logic becomes just as complex as any coded system. And that’s usually the moment things start breaking.
2. When Everything Looks Good but Loads Slowly
One of the most frustrating feelings in DIY development is watching a beautiful design load painfully slow. You tweak things, delete things, move things, yet the speed barely improves.
The reason is usually a mix of:
- Too many nested elements
- Multiple components loading dynamic data at once
- Heavy images
- Inefficient API calls
And here’s a number worth keeping in mind. Google found that users start abandoning a site if it takes more than 3 seconds to load. Seconds might not seem like much, but online, every second is a chance to lose someone’s trust.
3. When Your Data Works at First but Falls Apart Later
Backend structure is the part most DIY builders underestimate. Everything looks fine in the beginning when you have only a few records. But as your app grows, incorrect data relationships start causing slow queries, broken filters, and even missing records.
Common issues include:
- Data stored in ways that can’t be searched efficiently
- Overuse of relational tables
- Missing indexes
- Queries that strain your backend
These problems rarely show up immediately. They appear when you finally have real users, which makes them even harder to untangle.
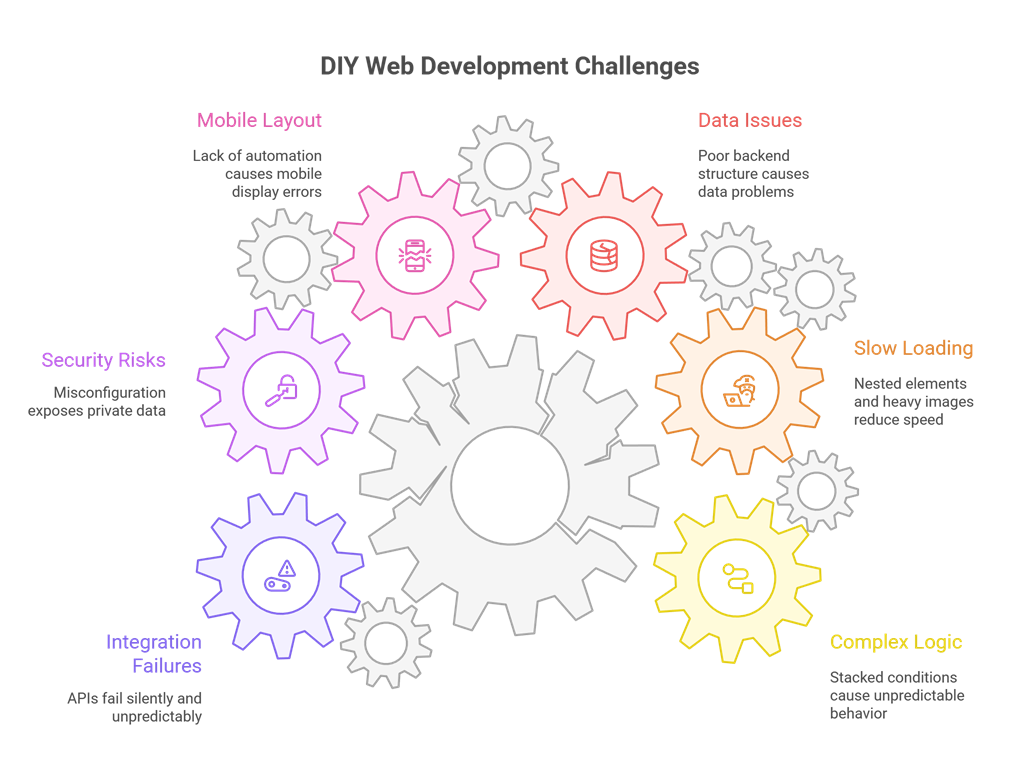
4. When Your Mobile Layout Just Doesn’t Look Right
You finish designing your desktop layout and it looks perfect. But then you check it on your phone and suddenly everything is off. Text overlaps. Buttons shift. Rows collapse strangely.
This happens to almost everyone because WeWeb gives you a lot of freedom, but not much automation. And with more than 70 percent of visitors judging a website based on its mobile experience, this becomes a deal breaker quickly.
5. When Security Becomes a Serious Concern
DIY builders often forget that even a small misconfiguration can expose private data.
Common oversights include:
- Public access to protected routes
- APIs left open
- Sensitive data revealed in workflows
- Authentication not set up properly
Security issues don’t always show obvious symptoms. They just quietly exist until something goes wrong. That is why apps handling personal or financial information almost always require professional review.
6. When Integrations Start Misbehaving
Connecting APIs, authentication systems, or third party tools is where most DIY builders reach their breaking point. Some days everything works perfectly, and the next day something silently fails without explanation.
This is when many people finally reach out to a software development company in USA because integration failures are incredibly time consuming and require technical understanding to diagnose.
When You Should Call a Professional
There is no shame in asking for help. In fact, the smartest founders and business owners reach out sooner rather than later because they understand the value of expertise. And if you want a team that already knows the common pitfalls and the fastest path to a stable, high performing WeWeb build, YES IT Labs is one of the smartest choices you can make. Here are the clearest signs that bringing in a WeWeb expert will move your project forward faster.
1. Your App Needs More Than Simple Buttons and Pages
Membership systems, dashboards, multi step logic, and filtered data views are powerful features. But they also require solid architecture behind the scenes. A professional can set them up properly from the beginning, saving you weeks of rebuilding later.
2. You Want Your App to Feel Smooth and Fast
WeWeb experts know tricks most DIY users never discover, from optimizing queries to restructuring layouts so they render more efficiently. A fast app changes how users perceive your brand.
3. You Keep Running Into API or Login Issues
Much of integration work relies on understanding how data behaves under different conditions. A pro can test every scenario and ensure stability long term.
4. You Want a Clean, Beautiful, Trustworthy Design
Design isn’t just aesthetics. It’s psychology. A clean layout instantly builds trust. A cluttered one raises doubts. Studies show that most people make a judgment about a website within a fraction of a second, purely based on design.
5. You Are Spending Hours Fixing What Should Take Minutes
If you are stuck watching tutorials, reopening the same workflow five times, and still not finding what’s wrong, that’s your signal. Professionals solve these problems daily. What takes you eight hours might take them twenty minutes.
Final Thoughts
DIY WeWeb development is empowering. It lets you experiment, create, and bring ideas to life without waiting on a developer. But at some point, most builders reach a wall. And that’s perfectly normal.
As your app grows, so does the complexity. Performance, security, data structure, and integrations all demand precision. Bringing in a professional doesn’t take away your control. It simply gives your project a stronger foundation, protects your time, and ensures your product is ready for real users.